mj-crabtree.github.io
Google Cloud Platform: A Presentation
Slide 1 : Kim
Google Cloud, or to be more precise, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a cloud computing suite created by Google, its first tools having been first launched almost fifteen years ago.
Slide 2 : Kim
Contents :
- Introduction
- Examples and details
- Use scenario and pros / cons of GCP
Slide 3 : Kim

Google Cloud Platform (GCP), provided by Google, encompasses a collection of cloud computing services that operate on the identical infrastructure utilized by Google for its consumer-facing offerings, including Google Search, Gmail, Google Drive, and YouTube. In addition to a suite of administrative utilities, GCP furnishes a range of individual cloud services that can be flexibly combined, encompassing computing, data storage, data analysis, and machine learning capabilities. Some well known companies who use Google Cloud include Verizon, LinkedIn, Facebook, eBay, The New York Times, Gitlab…
Slide 4 : Matthew
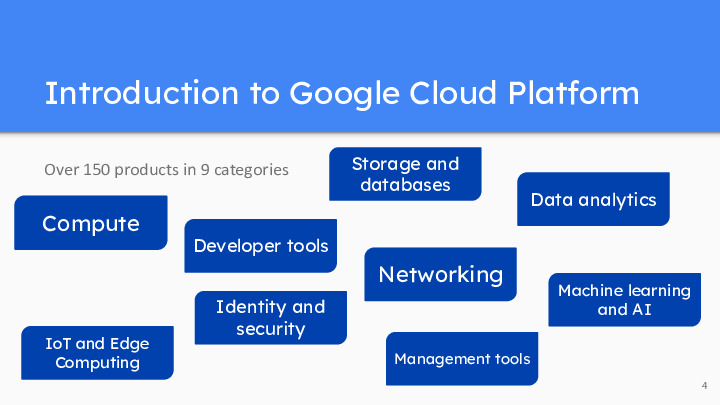
Over 150 products that we can split in 9 categories
- Compute: GCP provides computing resources, including App Engine, a Platform as a Service to deploy applications in various languages, virtual machines (VMs) through Compute Engine, managed Kubernetes clusters with Kubernetes Engine, serverless computing with Cloud Functions, an executive environment with Cloud Run…
- Developer Tools: GCP offers tools like Cloud Source Repositories for version control, Cloud Build for continuous integration and delivery, and Cloud Debugger for debugging applications.
- Storage and databases : It offers various data storage solutions such as Cloud Storage for object storage, Cloud SQL for managed relational databases, and Cloud Bigtable for NoSQL databases, but also Cloud Spanner or Firestore…
- Data Analytics: GCP includes BigQuery for real-time data analytics, Dataflow for stream and batch data processing, Dataprep for data preparation and cleaning, Cloud Pub/Sub for dealing with events, Looker for dashboards and dataviz…
- Machine Learning and AI: Google Cloud offers a robust suite of machine learning and AI tools, including AutoML for custom machine learning models, AI Platform for model development and deployment, and Vision AI and Natural Language AI for image and text analysis.
- Networking: GCP provides networking services like Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) for secure network isolation, Cloud Load Balancing for distributing traffic, and Cloud CDN for content delivery.
- Identity and Security: Identity and Access Management (IAM) allows you to control access to resources, and GCP provides security services like Cloud Security Command Center and Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP).
- IoT and Edge Computing: Google Cloud IoT Core enables the management and ingestion of IoT data, and Edge TPU provides hardware accelerators for edge AI.
- Management tools: Google Cloud Platform offers a range of management tools, including Operations suite for monitoring and diagnostics, Cloud Console for web-based resource management, Cloud Shell for browser-based command-line access, and Cloud APIs for programmatic access to GCP resources.
Slide 5 : Emile
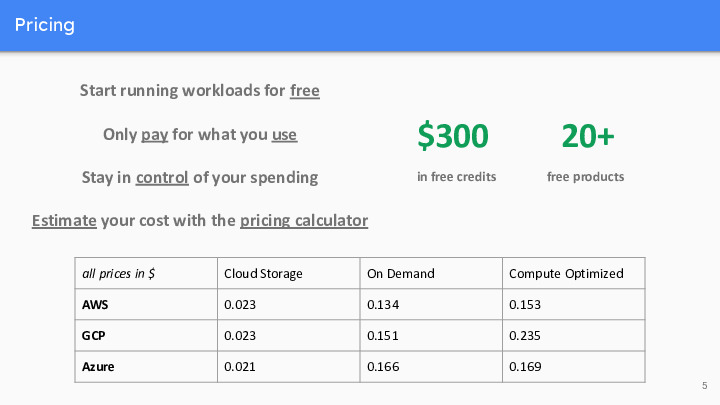
Pricing
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers competitive pricing compared to its major competitors, AWS and Azure. One key advantage is the ability to start running workloads for free, allowing users to get a taste of GCP without incurring initial costs. GCP’s “pay for what you use” model ensures cost efficiency, as you only pay for the resources consumed. The pricing calculator further aids in cost estimation and control. Comparing specific services, such as Cloud Storage and Compute Optimized instances, GCP’s prices align closely with AWS and Azure, making it a compelling choice for organizations looking to manage costs effectively while enjoying a wide range of cloud services.
Slide 6 : Matthew

We will now provide you with a few examples of what the Google Cloud Platform can do, by showing you briefly 5 of its tools : App Engine, BigQuery, Cloud Functions, Cloud Run and Cloud Monitoring.
Slide 7 to 10 : Xue
App Engine
first,let me introduce Google App Engine,Google App Engine is a platform that allows you to run your network applications on Google’s infrastructure. The Google App Engine application is easy to build and maintain, and can easily scale according to your access volume and data storage needs. With Google App Engine, you no longer need to maintain servers: you just need to upload your application and it can immediately provide services to your users.

by using theGoogle App Engine。There is no need to manage servers or deploy configurations。
Maintain agility and mobility with support for numerous mainstream development languages and various developer tools。
Common programming languages: Node.js, Java, Ruby, C #, Go, Python, or PHP。
Fully managed: A fully managed environment allows you to focus on code writing and delegate infrastructure transactions to the App Engine for management.
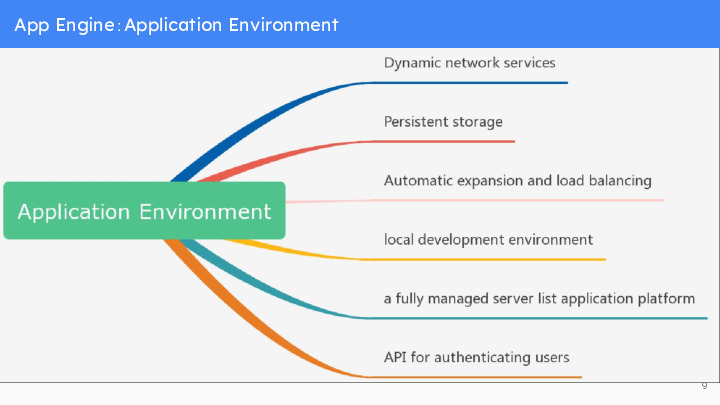
Through the Google App Engine, it is easy to build applications that can run safely even under heavy loads and large amounts of data.
Dynamic network services, providing full support for commonly used network technologies
Persistent storage includes queries, classifications, and transactions
Automatic expansion and load balancing
API for authenticating users and sending emails using Google accounts
A fully functional local development environment that can simulate Google App Engine on our own computer
Slide 10 to 14 : Kim

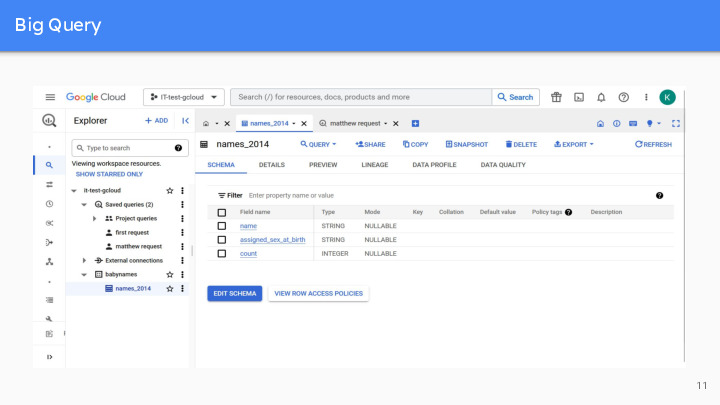
BigQuery is Google’s serverless data warehouse that enables analysis over large quantities of data. It is a PaaS (Platform as a Service) that supports queries using a dialect of SQL.
It is very easy to use and largely adopted in many companies. In addition to managing and querying data, BigQuery also offers tools for machine learning, data sharing, cross-cloud analytics, business intelligence, etc. Simple example to show you the user interface : count the names of babies born in 2014, large dataset added from a CSV file. We can visualize the fields names and their types, as well as details on the table and a preview of the data (the first lines).
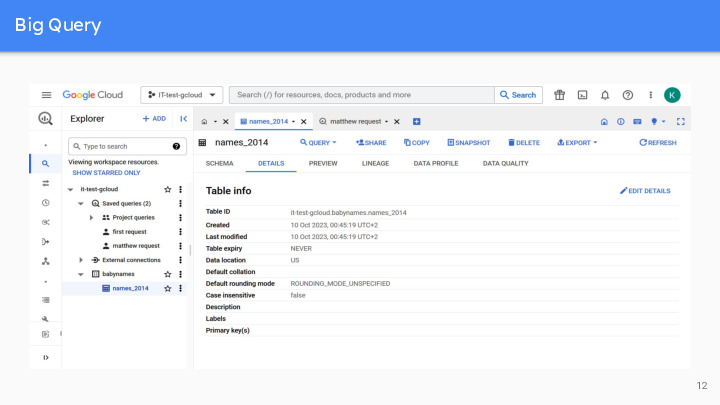
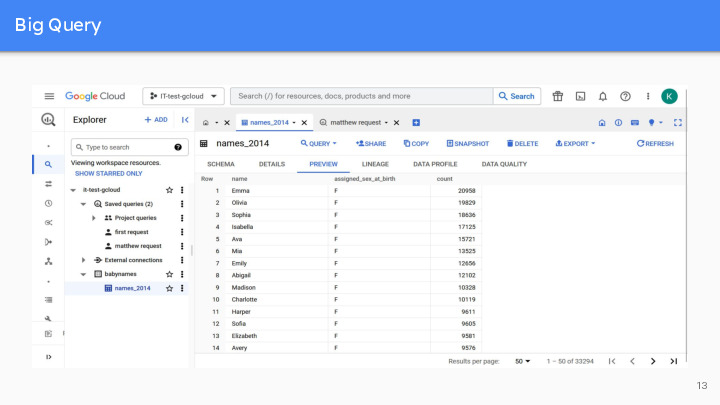
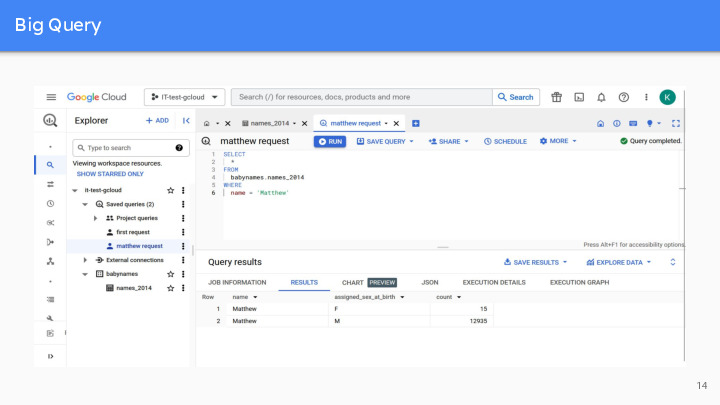
Slide 15 to 19 : Matthew

what?
First, we have Event-Driven Computing. With Google Cloud Functions, you can instantly respond to user-driven events in real-time. Whether it’s an HTTP request, a file upload, or changes in your cloud storage, this platform ensures your application stack reacts swiftly and seamlessly.
Next up, we have Serverless Code Execution. Imagine focusing solely on your code without the burden of managing the stack. Google Cloud Functions handles the infrastructure, allowing you to concentrate on writing your applications. It’s developer productivity at its finest.
Lastly, Management as a Service. Your cloud functions are automatically scaled up and down as needed. No more worries about infrastructure management. Your boss needs functionality? Write some code, deploy it immediately, let Google handle the rest– it’s that simple!
Two key features, here. Serverless developer experience, and event-driven design. If you understand these, you understand the benefit of Cloud Functions.
why?
Google Cloud Functions allows you to pay only for the compute resources you actually use, which can lead to significant cost savings. Since it automatically scales up or down based on your workload, you’re not paying for idle server time. This cost-efficiency makes it an attractive choice for businesses looking to optimize their cloud spending.
With Google Cloud Functions, your applications can seamlessly handle varying workloads. Whether you have a sudden surge in traffic or a drop in demand, the platform automatically scales resources to meet the demand.
You can write and deploy code quickly, responding to your business needs with agility. This rapid development cycle is particularly advantageous for startups, small teams, and organizations aiming to iterate and innovate at a faster pace. It accelerates the time-to-market for your applications and services.
how?
self evident. riff. throw in a joke.
NEXT
And now for a (very) quick look at how these things are implemented using .Net.

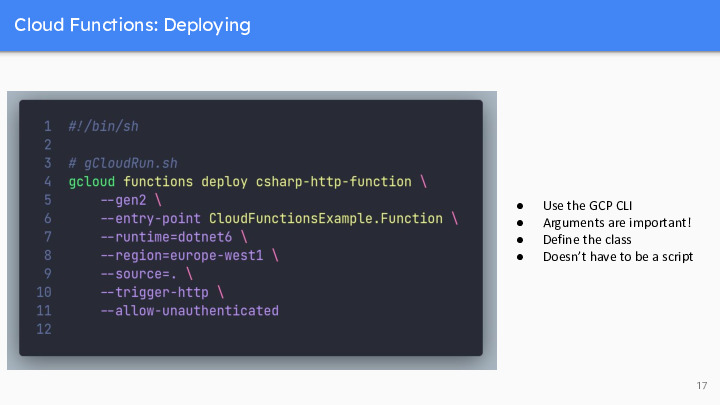
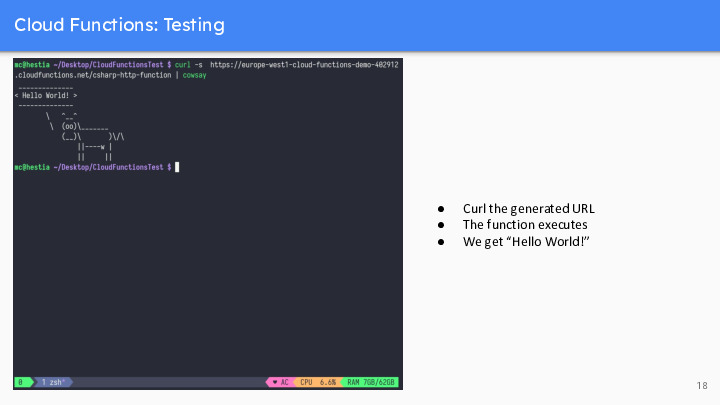
Slide 20 to 24 : Emile
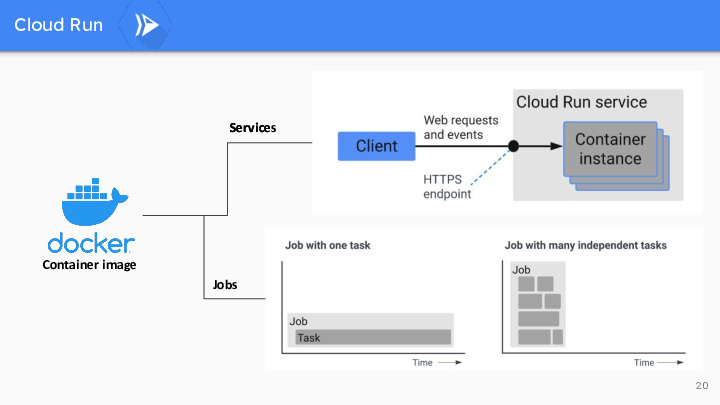
Cloud Run
Google Cloud Run is a serverless computing platform that allows developers to easily deploy and run containerized applications in a fully managed environment.
A container is a lightweight, stand-alone, executable software package that includes everything needed to run a piece of software, including the code, runtime, system tools, libraries, and settings.
In the context of cloud computing, a service typically refers to a long-running, stateful application that provides continuous functionality, while a job is a short-lived, stateless task executed for a specific purpose, often in a batch or on-demand manner. Services are persistent and handle ongoing requests, whereas jobs are temporary and used for specific, one-time operations.
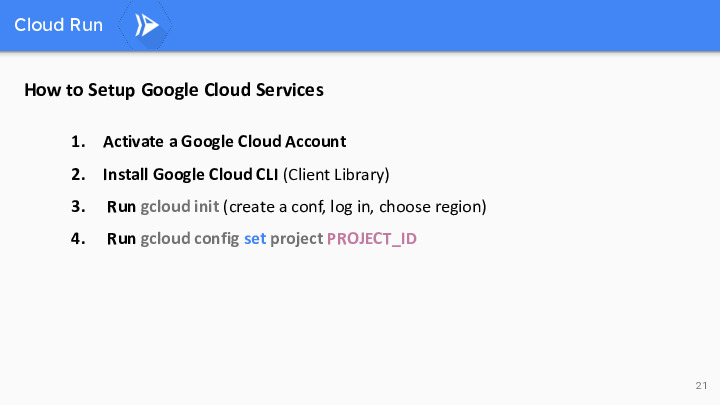
Setting up a Google Cloud service involves a straightforward process. First, you need to activate a Google Cloud account, which provides access to the platform’s resources. Next, install the Google Cloud CLI (Client Library) on your local machine. Once installed, run ‘gcloud init’ to create a configuration, log in to your Google Cloud account, and select a preferred region. Finally, specify the project you’re working on by running ‘gcloud config set project PROJECT_ID,’ ensuring that you’re connected to the correct project for your specific cloud service needs. This streamlined procedure allows you to quickly configure your Google Cloud environment and begin leveraging its powerful cloud services.

You’ll need the essential files, including ‘main.py,’ ‘requirements.txt,’ and a ‘Dockerfile’ for containerization. With these prerequisites in place, deploy your website using ‘gcloud run deploy.’ During deployment, you’ll need to provide the source code location, choose a service name, select a region, and decide whether to allow unauthenticated invocations. This comprehensive procedure ensures the smooth initiation of your Python3 Flask website project on Google Cloud Services.

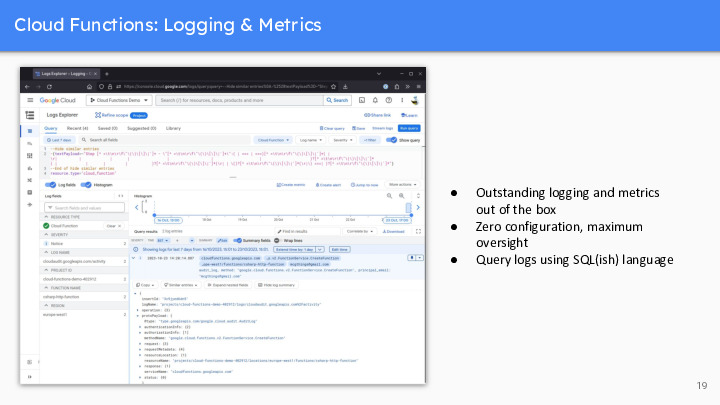
The log of a Google Cloud Run service provides a valuable trail of information, capturing real-time data and events, including application errors, request responses, and resource utilization. These logs are essential for monitoring and troubleshooting, enabling developers to gain insights into service performance and user interactions, ensuring a seamless and reliable application experience.
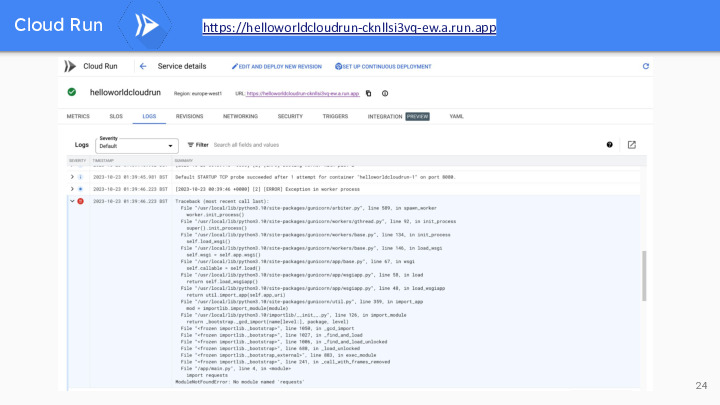
https://helloworldcloudrun-cknllsi3vq-ew.a.run.app
Slide 25 to 29 : Wang
Cloud Monitoring
Cloud Monitoring is a service provided by GCP for monitoring and managing the performance and availability of cloud infrastructure, applications, and services.
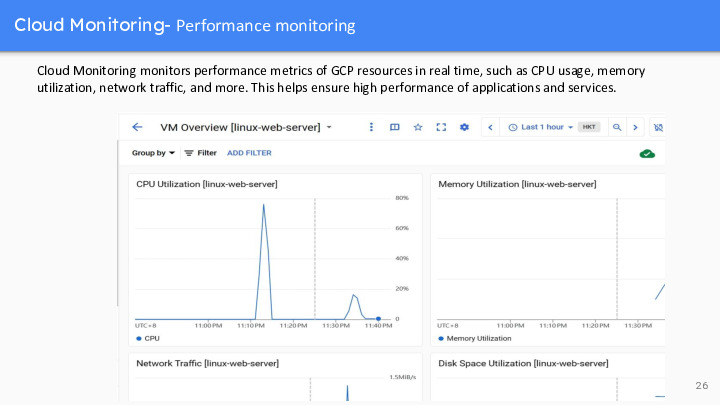
Cloud monitoring provides real-time performance and health monitoring, enabling users to quickly identify issues and take action. Cloud Monitoring monitors performance metrics of GCP resources in real time, such as CPU usage, memory utilization, network traffic, and more. This helps ensure high performance of applications and services. Like the picture I posted on the right, I created a virtual machine and monitored it. From this picture, we can clearly see the cpu usage, memory usage, network traffic and so on of the virtual machine.
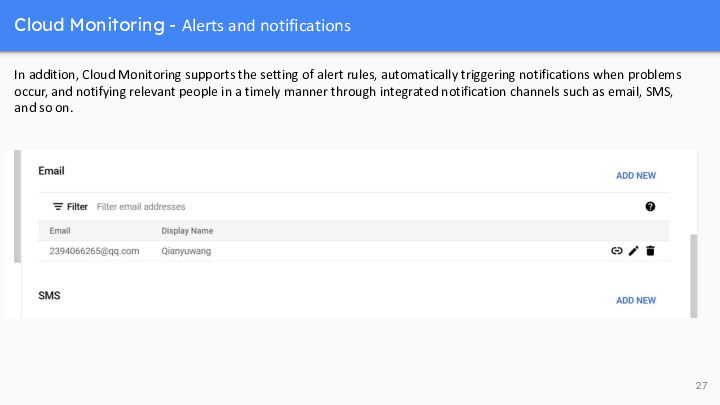
In addition, Cloud Monitoring supports the setting of alert rules, automatically triggering notifications when problems occur, and notifying relevant people in a timely manner through integrated notification channels such as email, SMS, and so on.
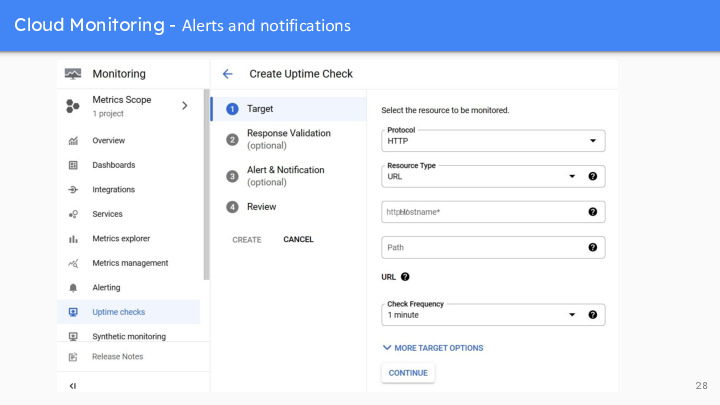
You can set up alert rules for resources, and the system will send you notifications when performance metrics exceed specified thresholds(阈值), which helps to find and resolve problems in a timely manner.By setting up alert rules, you can monitor the performance of cloud resources in real time without manually checking or waiting for problems to become apparent(显而易见的). This helps you spot potential problems in a timely manner so that you can take action to prevent potential performance degradation(衰退) or availability issues. With this automated approach, you can manage and maintain your cloud environment more efficiently, ensuring the reliability and high availability of your services
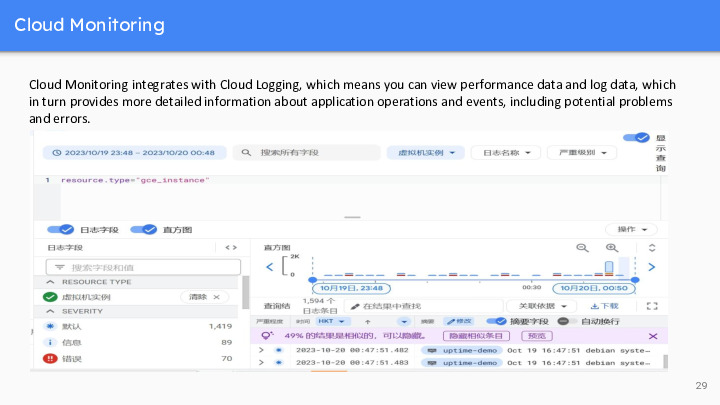
Cloud Monitoring integrates with Cloud Logging, which means you can view performance data and log data, which in turn provides more detailed information about application operations and events, including potential problems and errors. Cloud Logging captures a variety of log data, including application logs, system logs, and security logs. This log data provides detailed information about the internal workings of the application, as well as potential exceptions
Slide 30 and 31 : Kim
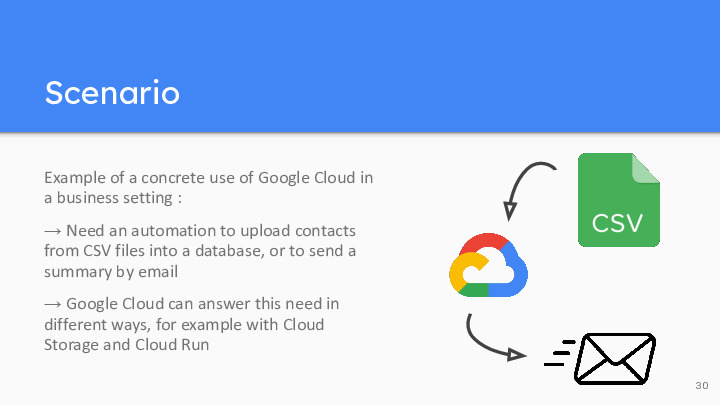
Example of a concrete use of Google Cloud in a business setting :
Need for an automation to upload contacts from CSV files into a database, or to send a summary by email. This need is inspired by a real problem that a company needed to solve during my last internship. It could be for example for a sales team who receive contacts of potential clients through CSV files, and who need to have an easy way to classify them, check the validity of the email address, and maybe import them in their database… We won’t consider the database import, but rather sending a summary by email.
Google Cloud can answer this needs in different ways, for example with Cloud Storage and Cloud Run
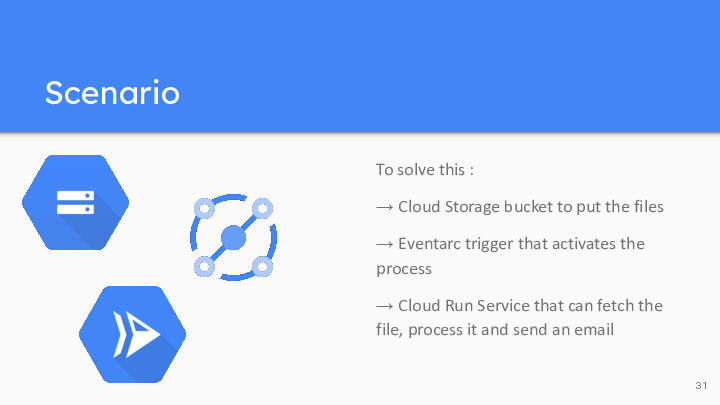
So one way to solve this is to first use a Cloud Storage bucket (which is basically a folder) to put the files. Then we can implement an Eventarc trigger that is set off every time a file is added into the bucket. This eventarc trigger activates a Cloud Run service through a request. This request holds the name of the file, so the service can fetch it, access it, and process the data. For example, the service can keep only contacts with a valid-looking email, and classify them in different countries / domains, and then send an email to a specified address with the summary.
We implemented this scenario in Python on Google Cloud and with sample contacts csv files, and you will be able to find the detailed tutorial on our last document.
This is a real life example, quite useful, but not very big. One of the advantages of Google Cloud is that it offers so many tools and possibilities ! We’re getting closer to the end of our presentation, so i’ll just let Emile present to you the pros and cons of Google Cloud.
Slide 32 : Emile

Pros:
Data and Analytics: GCP has strong capabilities in data analytics and machine learning with BigQuery and AI/ML services like TensorFlow. It’s a preferred choice for data-intensive workloads.
Pricing and Flexibility: GCP often offers competitive pricing and a per-second billing model. It provides discounts for sustained usage and custom machine types.
Global Network: Google has an extensive global network infrastructure, offering fast and reliable connections, particularly beneficial for global users.
Open Source: GCP supports many open-source technologies, making it a choice for developers who favor open-source solutions.
Kubernetes Expertise: Google is the original creator of Kubernetes, and GCP provides strong support for container orchestration with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
Cons:
Smaller Market Share: GCP has a smaller market share compared to AWS and Azure, which can result in fewer available third-party integrations and community resources.
Learning Curve: Transitioning to GCP may require some learning, and there might be fewer resources compared to AWS and Azure.
Service Portfolio: While GCP’s service offerings are extensive, they may not be as broad as those of AWS and Azure.